Silicon carbide (SiC) is a compound widely recognized for its remarkable properties and versatility across various industries. As an essential semiconductor material, it plays a pivotal role in the advancement of modern technology, particularly in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles, power electronics, and renewable energy systems. According to a recent market report by Research and Markets, the silicon carbide market is projected to reach over $5 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 30% due to increased demand for energy-efficient components.
Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in materials science, emphasizes the significance of understanding "Silicon Carbide Meaning" in today's technological landscape. She states, "Silicon carbide is not just a material; it represents a leap towards sustainable technology, enabling higher efficiency and lower energy losses." This statement underlines the transformative potential of silicon carbide in empowering industries to meet the growing demand for sustainable solutions.
As we delve into the meaning, uses, and benefits of silicon carbide, it becomes clear that its unique properties, including thermal conductivity, exceptional hardness, and high electrical resistivity, make it an invaluable asset for future innovations. Understanding silicon carbide's meaning will help industry stakeholders harness its potential to drive performance and efficiency across diverse applications.

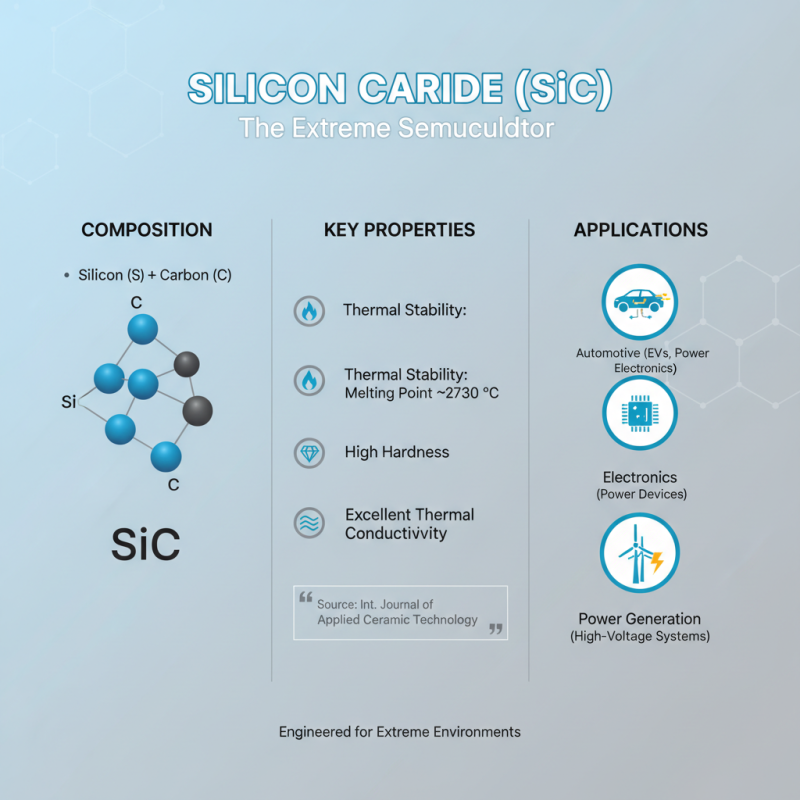
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a compound semiconductor that consists of silicon and carbon, forming a crystalline structure known for its impressive thermal and chemical stability. Its chemical formula, SiC, indicates that each silicon atom is bonded to a carbon atom, creating a robust lattice that exhibits high hardness and thermal conductivity. According to the International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, SiC has a melting point of around 2,730 °C, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Its unique properties enable its extensive use in various industries, including automotive, electronics, and power generation.
In terms of applications, silicon carbide plays a vital role in enhancing the efficiency of power devices. For instance, SiC-based power MOSFETs demonstrate lower energy losses compared to traditional silicon-based devices, leading to improved performance in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. A report from the Semiconductor Industry Association highlights that the market for SiC power devices is projected to grow significantly, reaching approximately $3.4 billion by 2025, driven largely by the increasing demand for efficient energy solutions.
Tips for utilizing silicon carbide technology effectively include ensuring proper thermal management in device designs to leverage SiC's superior thermal properties, and considering its high hardness when implementing SiC in abrasive applications. Additionally, staying informed about the latest advancements in SiC research can lead to more innovative applications across various fields.
Silicon carbide (SiC) was first discovered in 1891 by the American inventor Edward Goodrich Acheson during his experiments with electric arc furnaces. Acheson was initially searching for a way to produce artificial diamond, but instead, he created a new compound that exhibited remarkable hardness and thermal stability. This discovery laid the groundwork for what would become an essential material in various industrial applications. Acheson went on to establish the first commercial production of silicon carbide, which sparked interest in its properties and potential uses.
Over the following decades, silicon carbide underwent significant development, both in its production methods and applications. Initially utilized as an abrasive in grinding wheels and cutting tools, its unique properties gradually attracted attention from industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace. The material's ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments made it particularly valuable in semiconductor technology, leading to advancements in high-power electronic devices. As research continued, the production techniques improved, allowing for the creation of high-purity SiC crystals and paving the way for innovative applications in modern electronics and renewable energy systems.
Silicon carbide (SiC) has emerged as a crucial material across various industries due to its unique properties such as high thermal conductivity, exceptional hardness, and chemical resistance. In the semiconductor industry, SiC is increasingly being favored for power electronics applications. According to a report by Yole Développement, the silicon carbide semiconductor market is expected to reach approximately $4.65 billion by 2025, driven by the demand for more efficient energy solutions and the integration of renewable energy sources. This surge is primarily attributed to SiC's ability to handle high voltages and temperatures, making it ideal for electric vehicles (EVs), solar inverters, and industrial power supply systems.
In the automotive sector, silicon carbide's application is transformative, particularly in electric drivetrains. A study from the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that the efficiency of EVs can be significantly improved by incorporating SiC-based components, leading to longer range and reduced charging times. Moreover, SiC is utilized in the manufacturing of high-performance ceramics and abrasives due to its outstanding wear resistance. The trend of adopting SiC in manufacturing processes is set to grow, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 20% in ceramics usage by 2026, thereby enhancing product longevity and performance across diverse applications.
Silicon carbide (SiC) has gained significant traction in various industries due to its exceptional performance and efficiency benefits. As a semiconductor material, SiC operates at higher voltages, temperatures, and frequencies than traditional silicon, making it ideal for applications in power electronics. According to a report from "IDTechEx," the market for SiC devices is projected to reach $2.4 billion by 2025, driven primarily by its use in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial applications.
One of the most notable advantages of silicon carbide is its ability to improve energy efficiency. SiC devices exhibit lower switching losses and thermal resistance, allowing for more efficient power management. This efficiency translates into longer operating lifespans and reduced cooling requirements, which are crucial in high-performance applications. Research indicates that adopting SiC technology can lead to energy savings of up to 30% in certain applications, further enhancing the overall sustainability of energy use.
Tips for businesses considering silicon carbide include evaluating the total cost of ownership. While the initial investment may be higher compared to standard silicon solutions, the potential for operational savings due to energy efficiency and reduced maintenance can yield a favorable return on investment. Additionally, it is essential to stay updated with ongoing advancements in SiC technology, as emerging innovations may unlock even greater performance benefits.
| Property | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat dissipation. | Improves performance and extends the lifetime of electronic devices. |
| Electrical Properties | Wide bandgap semiconductor providing high breakdown voltage. | Enhances efficiency in power electronics and enables high-voltage applications. |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion. | Suitable for harsh environments, reducing maintenance costs. |
| Mechanical Properties | High hardness and excellent wear resistance. | Improves durability and extends the lifespan of components. |
| Applications | Used in power electronics, LED technology, and automotive sectors. | Facilitates advancements in energy efficiency and compact designs. |
The future trends in silicon carbide (SiC) technology are poised to revolutionize various industries, particularly in power electronics and electric vehicles. As global demand for energy-efficient solutions rises, the silicon carbide market is projected to grow significantly, with a market value forecasted to reach approximately $4 billion by 2026, according to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets. This surge is attributed to SiC's superior thermal conductivity, high voltage tolerance, and ability to operate at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Innovations in SiC technology are advancing rapidly, with research focusing on enhancing the material properties and manufacturing processes. For instance, the development of more cost-effective manufacturing techniques is expected to drive down prices and expand SiC's adoption in mainstream applications. Furthermore, noteworthy advancements in wafer sizes are paving the way for larger-scale production, significantly improving performance metrics for power devices. Industry analysts predict that by 2025, the automotive sector will account for a substantial portion of SiC demand, driven by the increasing integration of SiC-based components in electric drivetrains, which can improve efficiency by up to 30% compared to traditional silicon-based solutions. This intersection of innovation and demand highlights the critical role that silicon carbide will play in shaping a more sustainable energy landscape.