In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology and manufacturing, understanding the "Silicon Carbide Meaning" has become increasingly vital for industries poised for growth by 2025. Experts like Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority in semiconductor materials, articulate the significance of silicon carbide, stating, "Silicon carbide is not just a material; it's a gateway to enhancing efficiency and sustainability in various top industries." This statement encapsulates the transformative potential of silicon carbide in applications ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy solutions.
As businesses and researchers delve deeper into the properties and applications of silicon carbide, it is clear that this material's unique characteristics—such as its ability to withstand high temperatures and voltages—position it as a critical component in next-generation technologies. The understanding of "Silicon Carbide Meaning" is essential for industry leaders aiming to leverage its advantages for competitive breakthroughs. With a projected increase in demand, grasping this concept will enable stakeholders to capitalize on silicon carbide's capabilities for innovation and efficiency in their respective fields.

Silicon carbide (SiC) is a compound semiconductor that exhibits remarkable chemical properties, making it a crucial material for various industries. Composed of silicon and carbon, silicon carbide boasts a high level of thermal conductivity, outstanding hardness, and exceptional chemical stability, which makes it advantageous for applications that require resilience against harsh environments. According to a report from Materials Research Express, SiC has a Mohs hardness of 9, surpassing that of alumina and diamond, positioning it as an ideal choice for abrasive and cutting tools in industrial processes.
The importance of silicon carbide extends to its electrical properties as well. SiC has a wide bandgap of around 3.26 eV, which enables devices made from it to operate at higher voltages, temperatures, and frequencies compared to silicon-based devices. A report from Research and Markets indicates that the global silicon carbide market is projected to reach approximately USD 7.65 billion by 2025, driven largely by the semiconductor industry's shift towards more efficient energy solutions, particularly in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. The increasing demand for efficient power electronics not only highlights the versatility of silicon carbide but also its growing significance in shaping the future of top industries.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | SiC |
| Molar Mass | 40.1 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 2750 °C |
| Density | 3.21 g/cm³ |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 9-9.5 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 120-200 W/m·K |
| Applications | Semiconductors, LED technology, industrial machinery |
| Importance in 2025 | High efficiency in power electronics and renewable energy systems |
Silicon carbide (SiC) has a rich historical development that traces back to the late 19th century when it was first synthesized by Edward G. Acheson. Originally created as an abrasive material, SiC quickly found applications in various industrial processes due to its exceptional hardness and thermal stability. The early 20th century saw its use expand beyond abrasives to include applications in ceramics, semiconductors, and heating elements. This versatility made SiC a critical material in several manufacturing sectors, including glass, metallurgy, and optics.
In recent decades, the technological advancements have propelled the use of silicon carbide into innovative applications such as power electronics and renewable energy systems. Its wide bandgap allows for efficient energy conversion, making SiC a preferred material in high-performance devices. As industries transition towards greener technologies and more efficient power management solutions, the significance of silicon carbide continues to grow, particularly in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. As we approach 2025, SiC is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of emerging industries, driving efficiency and performance in various applications.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is emerging as a critical material across various industries, projected to see significant demand growth by 2025. This chart illustrates the expected demand for SiC in key sectors such as automotive, electronics, renewable energy, aerospace, and healthcare.
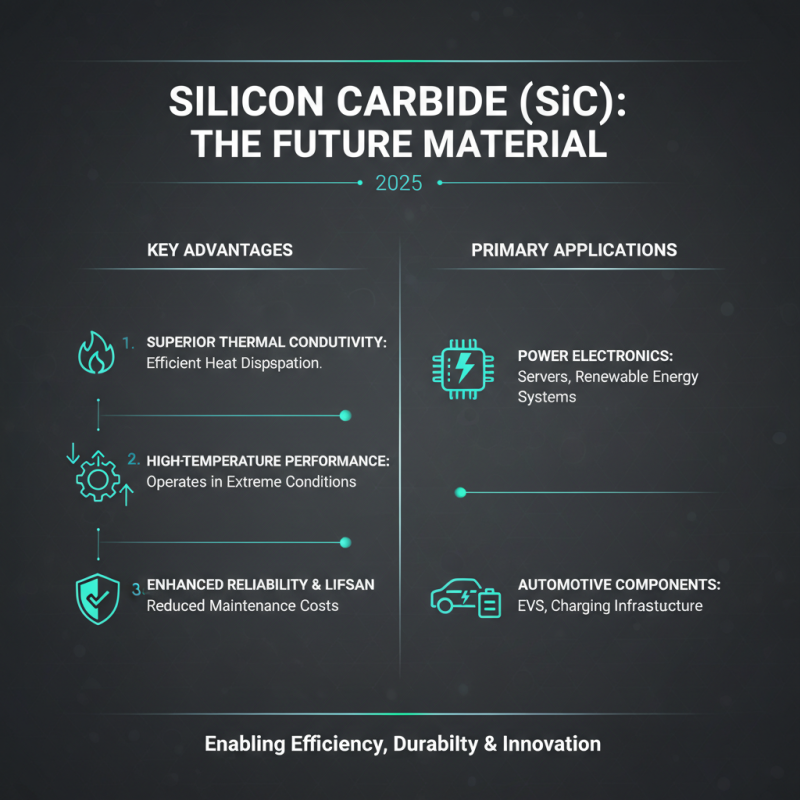
Silicon carbide (SiC) is emerging as a critical material for various industries in 2025, thanks to its remarkable properties. One of the key advantages of silicon carbide over traditional materials is its superior thermal conductivity. This property allows SiC to efficiently dissipate heat, making it ideal for high-temperature applications such as power electronics and automotive components. Its ability to maintain performance under extreme conditions translates to increased reliability and longer life cycles for devices, reducing maintenance costs over time.
Another significant benefit of silicon carbide is its high electrical breakdown field strength. This characteristic enables SiC components to operate at higher voltages, which is a crucial advantage in power conversion systems. By allowing devices to handle greater energy levels, silicon carbide is paving the way for advancements in renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles. Additionally, the lightweight nature of SiC reduces overall system weight, contributing to improved energy efficiency.
Tips: When considering the transition to silicon carbide in your projects, it’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of your applications. Always consult with materials experts to ensure optimal selection, and conduct thorough testing to experience the full range of benefits that silicon carbide can offer. Keep an eye on market trends, as innovation in SiC technology continues to evolve, potentially opening new opportunities for cost-effective and sustainable solutions.
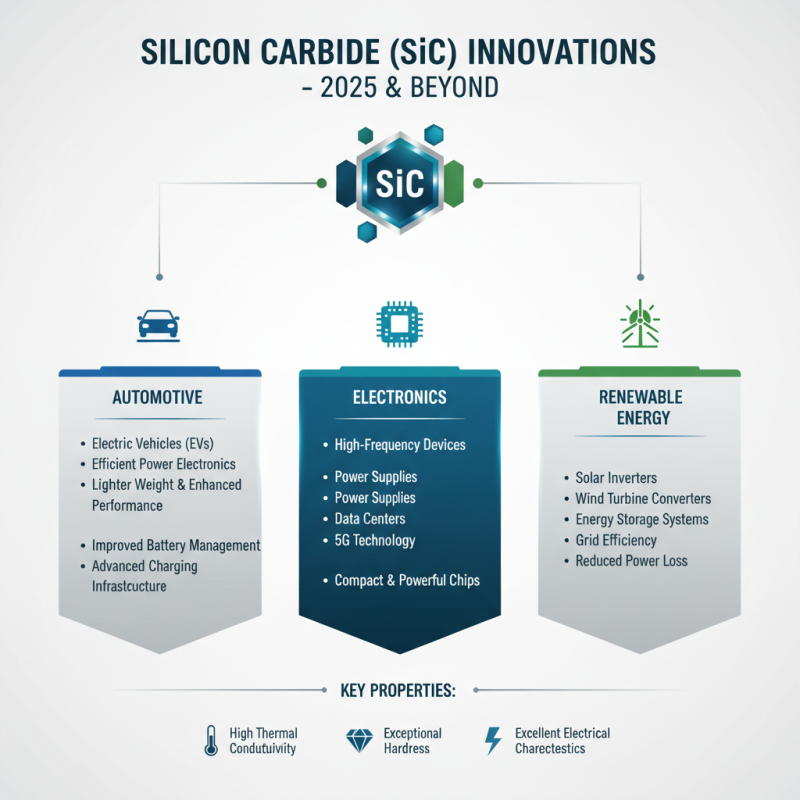
Silicon carbide (SiC) is emerging as a pivotal material in various industries due to its unique properties, such as high thermal conductivity, exceptional hardness, and excellent electrical characteristics. As we approach 2025, industries heavily impacted by SiC innovations include the automotive, electronics, and renewable energy sectors. In automotive applications, SiC enables the production of more efficient power electronics, promoting the growth of electric vehicles (EVs) with lighter weights and enhanced performance. With the automotive industry aggressively moving towards electrification, the role of SiC will be crucial in improving battery management systems and charging infrastructure.
In the electronics sector, the demand for faster and more efficient semiconductor devices is driving the adoption of silicon carbide. SiC transistors are capable of operating at higher voltages and temperatures, making them ideal for aerospace and defense applications as well. Furthermore, the renewable energy industry is set to benefit significantly from SiC technology through improved energy conversion systems. Solar inverters and wind turbine generators utilizing SiC components can achieve higher efficiency and reduced energy losses, thus facilitating a smoother transition to sustainable energy solutions. As these industries evolve, the importance of silicon carbide as a key enabler of innovation and efficiency will only continue to grow.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is rapidly emerging as a cornerstone material in several top industries, particularly in the context of growing energy efficiency and sustainability demands. By 2025, the market for silicon carbide is expected to reach approximately $6 billion, driven by its superior thermal conductivity and electric field performance. However, the transition towards this advanced material also presents significant trends and challenges. Notably, the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is a pivotal factor. As the automotive industry pivots to electrification, the need for robust semiconductor materials that support high voltages and temperatures continues to escalate.
One of the key trends is the increasing adoption of SiC power devices, which enhance the efficiency of energy conversion systems. Reports indicate that SiC devices can offer energy savings of up to 30% compared to traditional silicon devices, making them integral to modern power electronics. However, manufacturers face challenges in scaling production and ensuring the quality consistency of SiC wafers. Currently, the production cost remains a significant barrier, as high-quality SiC substrates are still more expensive to produce than their silicon counterparts.
Tips for adopting silicon carbide technology include focusing on collaboration within the supply chain and investing in R&D to overcome production hurdles. Additionally, education on SiC integration in existing systems can amplify its benefits in real-world applications. As industries continue to evolve, addressing these challenges while leveraging the advantages of silicon carbide will be crucial for maintaining competitiveness in the market.